The medical devices and diagnostics industry has experienced extensive growth, particularly catalyzed by the pandemic era, which brought rapid advancements and strategic partnerships. This period has resulted in significant innovation and transformation, pushing the boundaries of the life sciences industry. Moving forward, the industry can expect the realization of what once seemed like fictional treatments and technologies, continuing the transformative momentum initiated in the past few years.
Forces for transformation of Life Sciences industry
- Increased Outreach: pertaining to advances in transport and communication technology such as drone technology, that are enabling healthcare and product delivery to reach remote locations breaking geographical barriers,
- Medical Technology: various technologies along with Medical science are improving precision and efficiency, real-time monitoring, early detection and personalized treatment.
- Non-Conventional Product Development: use of computational modeling and generative design are expediting product innovation.
- Changed Landscape of Clinical Research: The paradigm shift towards digital twins, synthetic controls, and data-driven processes promotes decentralized trials and remote monitoring, offering more inclusive and efficient study designs.
- Faster Manufacturing: Robotic automation and 3D printing etc. are enabling rapid production scaling.
- Quality Assurance: AI-driven quality assurance and digital twin techniques are enhancing reliability lowering errors.
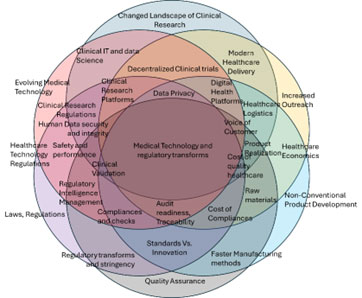
Figure 1: Complex relationship of the six-pillar life sciences landscape
Economy & business patterns
While Economy is not a direct contributor for transformation, it exerts a significant amount of progressive and confounding forces on the transformation in any field. However, a bitter but commercial fact is that this has built a pressure on startups to deliver ROI, which have led to compromises long-term R&D. Another challenge due to myopic investments in expectation of high returns caused market saturation and overvaluation of several Start-ups. The challenges related to the economy are forcing the transformation of various healthcare and life science business patterns to salvage the situation of lossmaking investments. Hence, the transformation success stories of other areas are explored for application to the Healthcare and Life sciences.
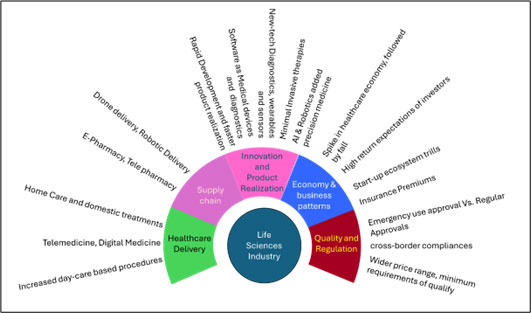
Fields of transformative impact in life sciences
The impact of growing technology, collaboration of various expertise and the current ear is laying down the fundamentals of quantum leap of transformation in the life sciences. Main areas where the primary transformation is expected include the Healthcare Delivery, Supply chain, Product Innovation and Product Realization, Healthcare economics and the healthcare business pattern and the quality and regulations. Each of these areas have both sides, viz. progressing and confounding forces in the transformation process. However, the resultant depends upon how these forces interact and what are their magnitude (Figure 1).
Figure 2: Fields of transformative impact in life sciences
Healthcare Delivery
Healthcare delivery has traditionally been an institution-bound affair, with most treatments and consultations taking place in hospitals or clinics. However, recent years have seen significant transformations in how healthcare services are delivered, driven by technological advancements, changing patient expectations, and societal shifts. Among the most popular transformations in healthcare delivery are telemedicine and digital medicine, which have emerged as pivotal elements in modern healthcare systems. As a pandemic response, the adoption of remote healthcare services is accelerated. Several factors contribute to the ongoing transformation in healthcare delivery:
- Availability Vs. Requirement: Healthcare in both developed and developing nations have a significant accessibility limitations.
- Technological Advancements: The development of telehealth platforms, AI, wearable devices, and mobile health apps has revolutionized healthcare services.
- Patient Expectations: Modern patients demand convenience and accessibility, prompting the adoption of digital solutions.
- Cost Efficiency: Telemedicine reduces overhead costs for healthcare facilities and patients alike.
Current and future trends in Healthcare Delivery revolve around –
- Telemedicine, Digital Medicine
- Home Care and domestic treatments
- Doorstep Diagnostics
- Robotic Telesurgery and Remote operative checks
- Next-gen Air ambulance and medical tourism
Benefits of these technological advancements in healthcare include increased accessibility for patients in remote areas, cost efficiency through reduced travel and operational costs, and personalized care via AI and genomics. However, these advancements also come with risks such as data privacy concerns, the digital divide, and resistance to change from traditional healthcare systems and professionals. Additionally, there are limitations including dependence on reliable internet and technology infrastructure, regulatory hurdles to ensure compliance with healthcare standards, and the irreplaceable human element in physical examinations and certain medical consultations.
Medical Supply chain
Medical Supply chain has rapidly moved from its traditional institution-bound affair through hospital’s stores and pharmacies. In recent years application and call-based prescription management and doorstep supply of the medicines has emerged and accelerated dramatically as a specialized service. The world also has witnessed surge in use of drones and robots in supply of goods including the medical materials, in the gone semidecade. The factors that favor this transformation are:
- Need of the hour: Increased requirement of unattended elderly care, especially when prescription and payment management require involvement of multiple users (e.g. doctor directly prescribing in the application or children of elderly people in India ordering from US)
- Technological Advancements: Mobile phones have made access easy and convenient for doorstep delivery applications. In addition, voice-commands and integrated home automation such as Alexa, and have made access to the services easy and simple.
- Timeliness and accuracy: Due to the availability of large stocks, most applications that provide doorstep delivery are more time efficient and accurate in supply of the medicines as prescribed by the doctor.
Current and future trends in Healthcare Delivery revolve around –
- Electronic Pharmacies integrated with doorstep testing or sample collection
- Drone Delivery and Robotic Delivery
Innovation and Product Realization
The rapid development and realization of medical devices and diagnostics are transforming healthcare. Digital twins and simulation tools enable precise virtual modeling, while agile processes ensure quicker market entry. 3D printing allows for custom medical devices and implants with high speed and accuracy. However, these advancements face challenges such as upholding quality standards, risks of intellectual property theft, and global supply chain disruptions. Importantly, faster product realization and robotic supply chains can synergize for just-in-time delivery yet face scaling and regulatory complexities.
The major impact of technology can be observed and anticipated to grow further in the following areas
- Rapid product development and faster product realization
- Software as Medical Device or Diagnostic, especially aided by cloud computing and big data integration.
- Minimally invasive therapies
- Rapidly progressing genomics and other omics
Quality and Regulation
Emergency Use Approvals versus Regular Approvals offer faster access to treatments during crises but risk compromised safety. Cross-Border Compliances bring global healthcare solutions but face complex regulatory requirements. A wider price range in medical products provides affordable options but risks market flooding with substandard items. Addressing these challenges requires robust global regulatory frameworks to maintain safety and efficacy while encouraging innovation.
Adopting new ways
Design Thinking in Biodesign for User-Centric Product Development
Biodesign enables innovative and accessible healthcare solutions and requires detailed understanding of patient needs, user requirements and iterative prototyping to ensure development of safe, effective, and user-friendly medical devices. Design thinking includes identification of persona, capability, and integration of feedback loops, interdisciplinary collaboration. Biodesign with design thinking applied together can lead to more innovative and accessible healthcare solutions. This approach fosters a more dynamic and responsive healthcare ecosystem, capable of quickly adapting to emerging needs and challenges.
Integration of agile methods and technologies like 3d printing, predictive AI, and digital twin next-gen sensors, IOT, expanded use of AI, wearable technology, genomics and translational medicine, lasers, advanced robotics, and other technologies
Integration of agile methods, data science and technologies is the key progressive force for transformation. However, challenges such as data interoperability, consumer mistrust, and ethical concerns in AI-driven decision-making must be addressed. Ensuring data privacy and transparency, alongside robust regulatory frameworks and cross-platform compatibility, is essential to overcoming these barriers. As healthcare systems become increasingly digital, addressing these issues will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of these transformative technologies.
A. Precision medicine, Companion biometrics and diagnostic, remote operative procedures
The integration of AI, wearable technology, genomic medicine, and advanced robotics have revolutionizing potential in comprehensive healthcare innovations and its real world application. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, personalization of treatment, and accuracy and precision and remote intervention. Wearable with advanced sensors have already proven value in continuous data capture, which, along with AI provide accurate alarms in risky conditions. Genomics and other omics have increased diagnostic precision while robotics have enhanced operative precision. Several aspects such as ingestible (may be inhalable in the future) and wirelessly controllable camera capsules can enable even complex diagnostics of the gut. The future, with some advanced wireless instrumentation can lead to remotely conducted procedures in minimal set-ups or even in the home set up.
B. For low cost of failure in product development and collaborative innovation
When it comes to technology, the method of development and the cost of failures are extremely critical factors for success. Like information technology, integration of agile methods and technologies that would help minimizing risks and cost of failure such as 3D printing and bioprinting, predictive AI, and digital twin provide cost efficiency in product development cycles. Use or excimer, dimer or polymer lasers are also transforming to various molecular experiments, including assessment of toxicology and biocompatibility of such materials and also is proving valuable in treatment of certain diseases. These technologies allow rapid prototyping, real-time data analysis, and accurate simulations, leading to rapid and streamlined the transition from concept to market.
C. For adoptative predictive translations of preclinical outcomes to clinical application
Preclinical data of pharmacology, bio-hemocompatibility, desktop testing, healthy and disease model animal studies for medical devices and other simulations are valuable data for clinical outcome of the final product in real world use. However, in lack of appropriate methods for translation of this data of the product to its real-world use, majority if its potential is unutilized and is limited to regulatory approvals alone. However, adoptative predictive translations of preclinical outcomes to clinical application may employ advanced modeling and simulation techniques, bio-physio-chemo-material response techniques (collectively can be labelled as silicatomics) and accurately translate the data of preclinical tests to predict at least the ranges of clinical outcomes. The silacatomics can evolve into a completely new branch of translational medicine and form a set of biomarkers that fosters low cost-high-success collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies and accelerates innovation of efficient, precise and safely therapies.
Newer biomaterials
Biomaterials is another important aspect of major transformation of the medical products. Introduction of various photochemical, electrochemical and bioelectrical or biomagnetic materials, biosimilars, stem cell, engineered genetic and synthetic tissues, tissue matrix materials, etc. along with the nano materials, plasma, serum and tissue proteins used as 3D printing inks etc. are the technologies in progress at various levels of maturity. Excimer, dimer and polymer laser in therapeutic applications, is already discussed. Certain specific materials and biomaterial technology which have evolved significantly in the healthcare segment include polymers, energies, various biological derivatives and nano technology.
Nano technology and Nano delivery systems
Innovations in nanotechnology are paving the way for advanced diagnostic tools and treatments including nano-robots offer precise targeting and controlled release of drugs at the cellular level, minimizing side effects and enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Newer Polymers, tissues and alloys in medical science
Advanced materials including biocompatible polymers engineered tissues and alloys are subject to next genre of revolutionized prosthetics and implants to create synthetic organs.
Newer applications of radiation and energies
Advanced radiation techniques and energies, including proton therapy, excimer or polymer lasers, ultrasound therapies, etc. are leading to precision and effectiveness of various medical procedures, surgeries, pain management and also development of drugs and devices.
Adaptive Quality assurance, risk management, Clinical Research and regulatory affairs for optimal quality and innovation
Newer Quality assurance, risk management, and regulatory affairs for optimal quality and innovation. These disciplines ensure that medical devices meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy. They are critical in mitigating risks and facilitating compliance with global regulatory requirements. By systematically addressing potential hazards, industry can foster a culture of continuous improvement. This, in turn, encourages the development of cutting-edge technologies that push the boundaries of modern medicine.
Increasing heath-centric education for better availability of resource
Increasing health-centric education, training programs are critical aid for transforming the sector and stay ahead of challenges and leverage innovations for better patient outcomes.
Collaborative and harmonized regulation and medical education
Collaborative regulatory and harmonized medical education is required to meet and streamline innovations, especially the cross-border regulatory requirements for medical practice and swift adaptation to emerging technologies and allow Refurbishing, reprocessing and reuse of medical devices.
Insurance
Innovative insurance models to include the newer and specific digital healthcare needs, and cover any losses of the investors, allowing non-restrictive revolutionization in technology.